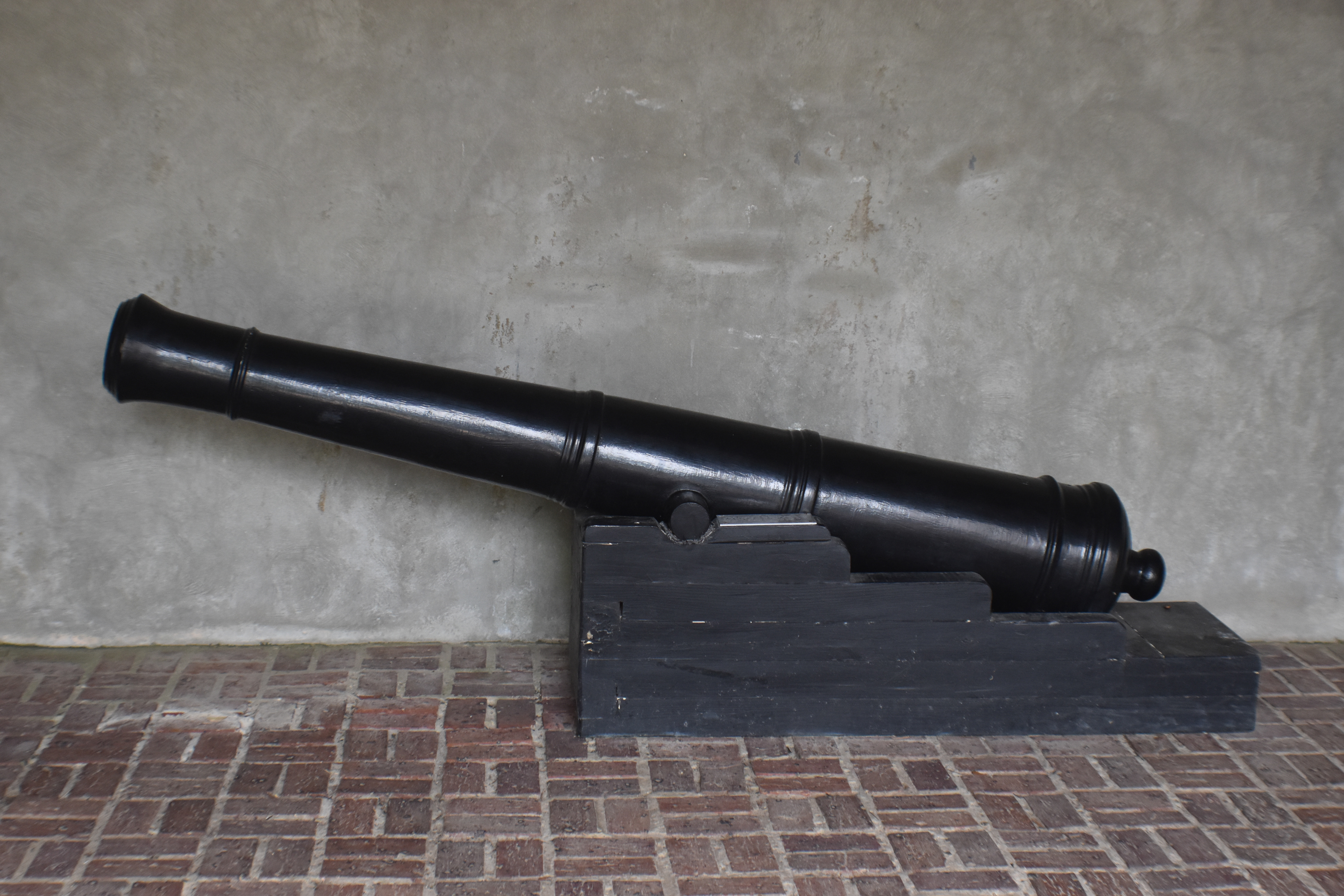
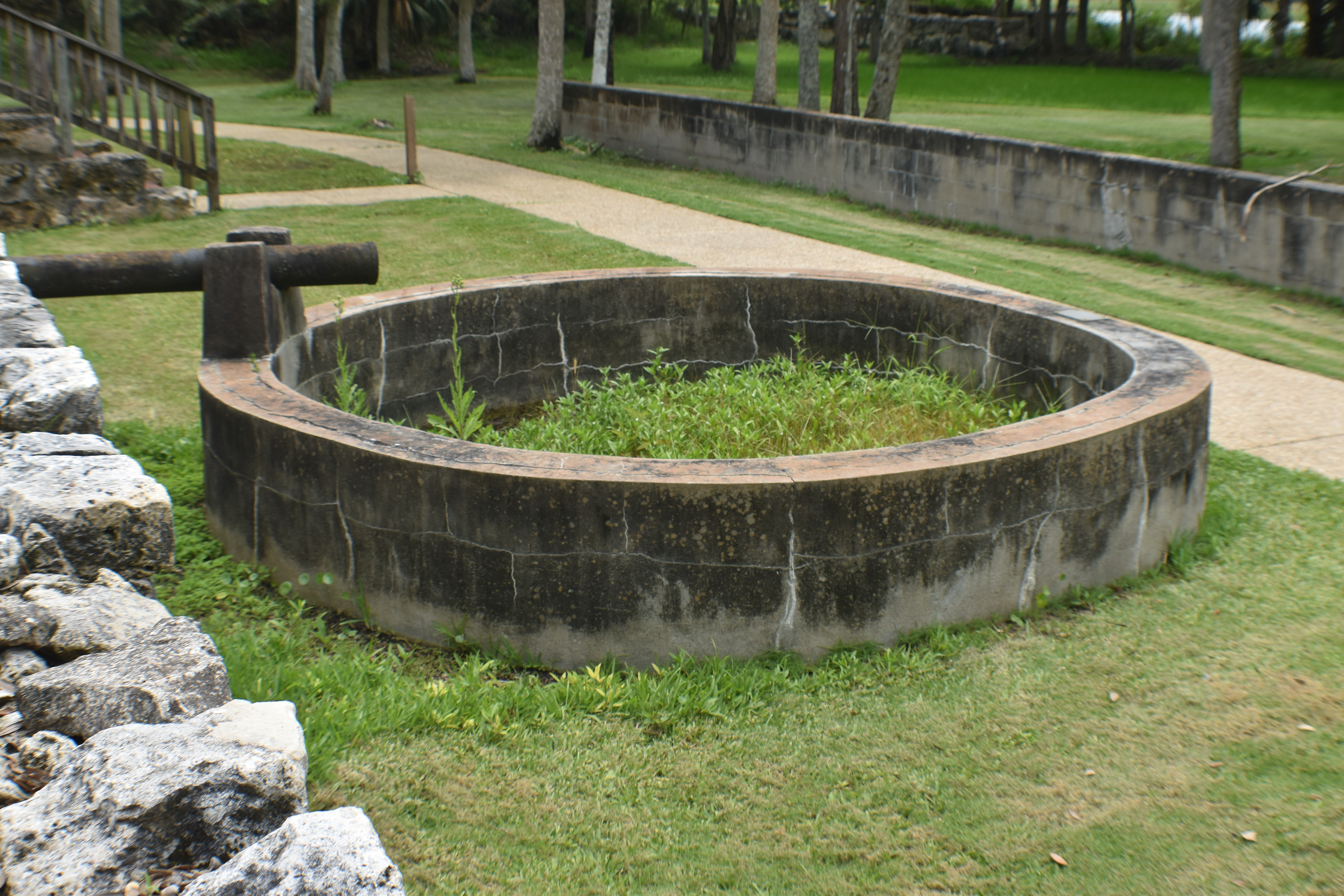
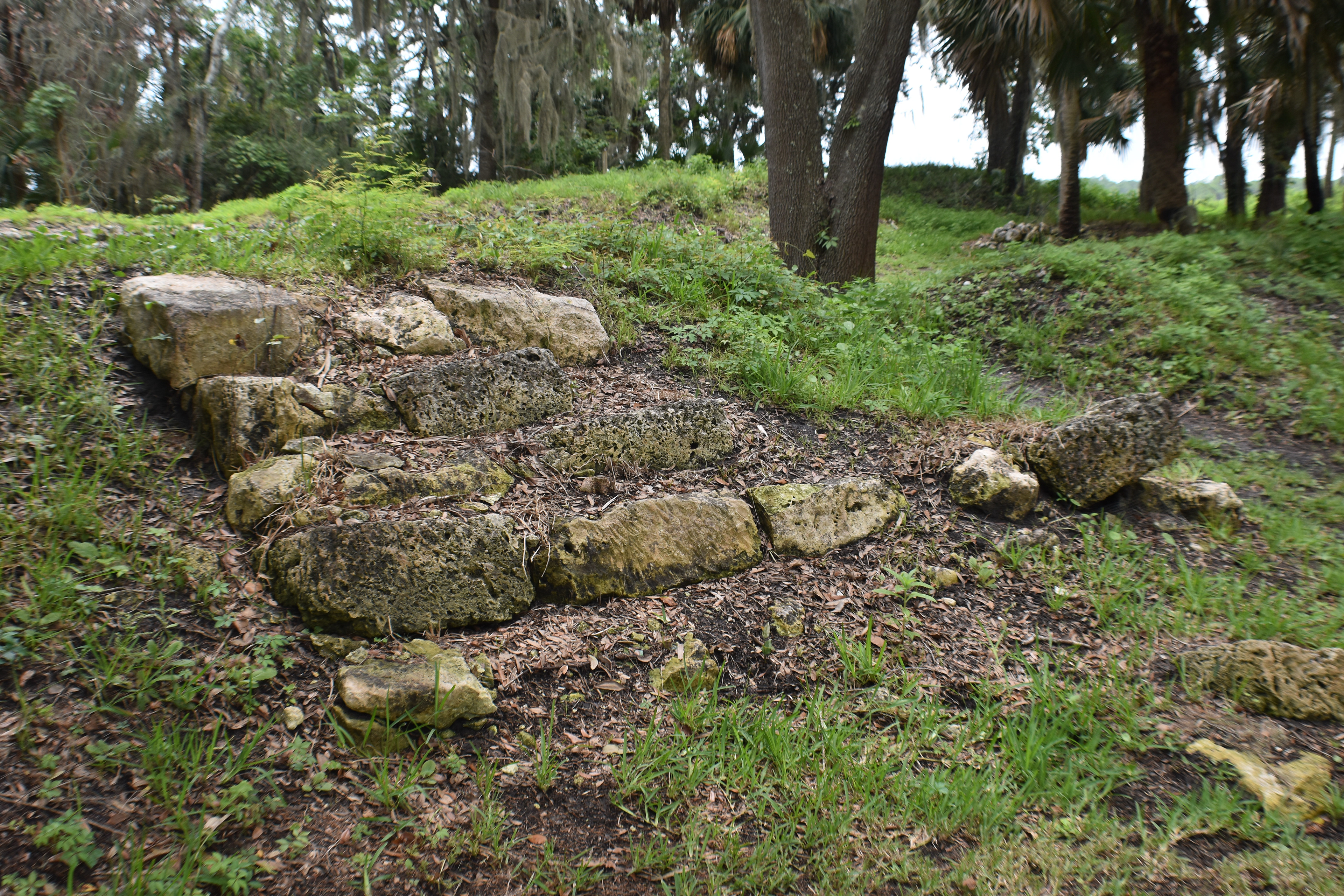
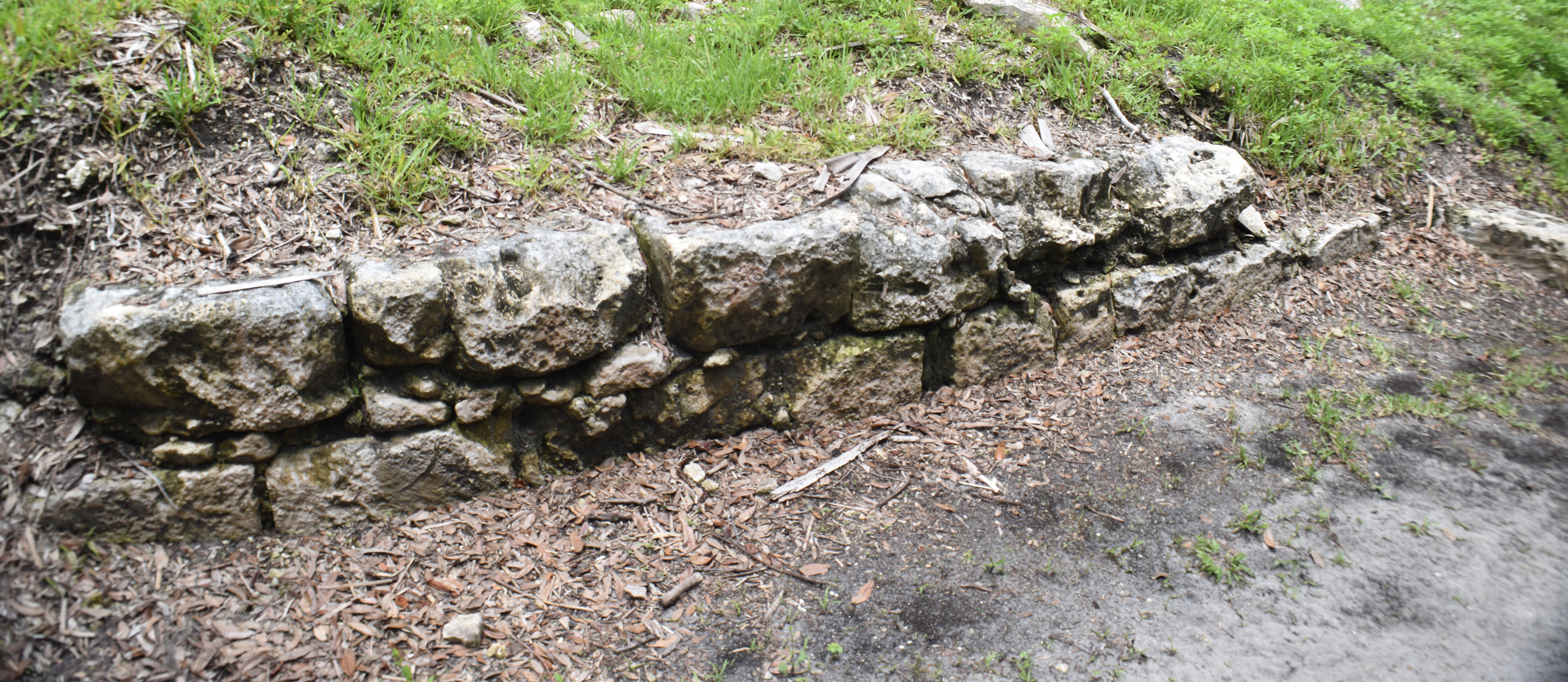
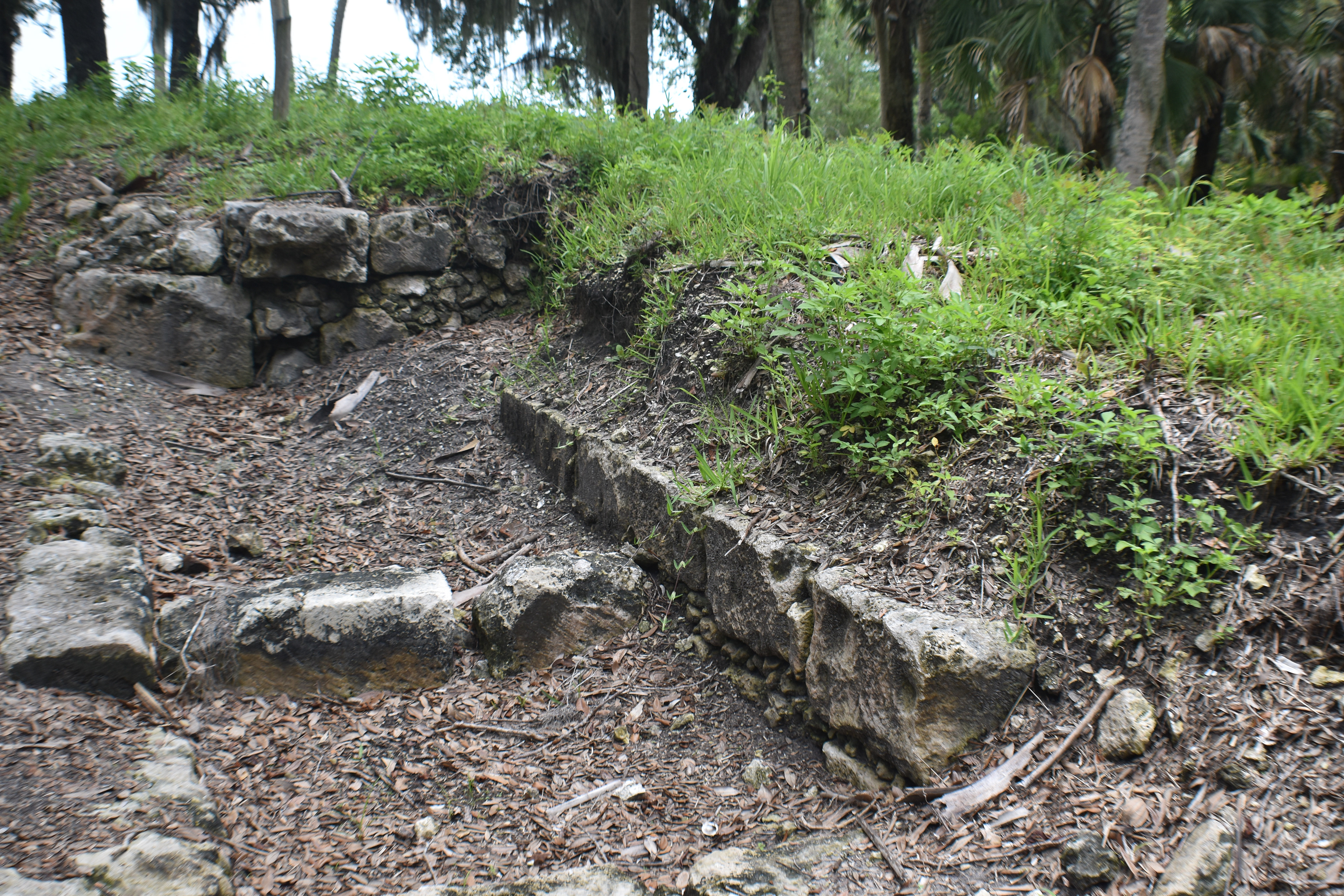
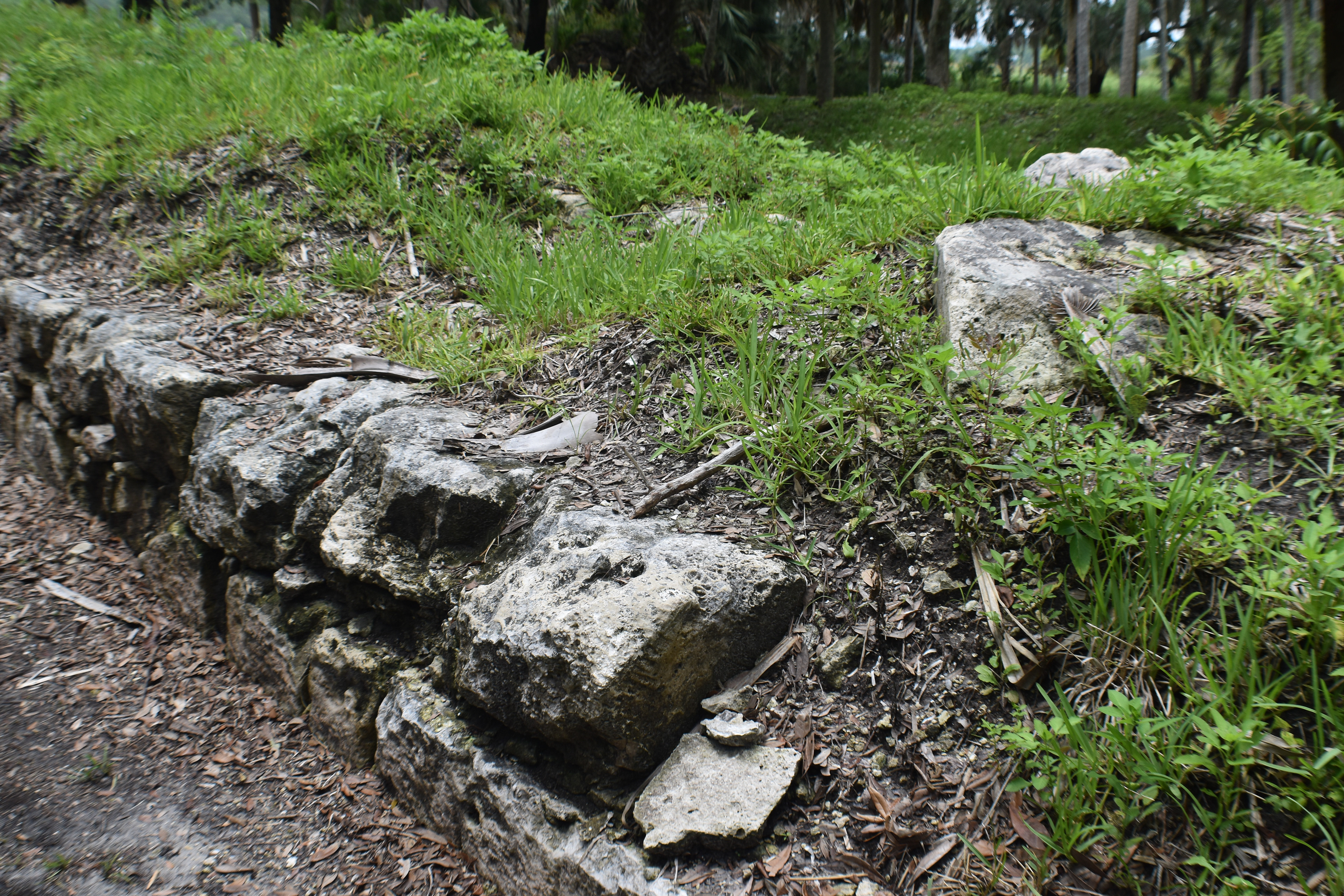
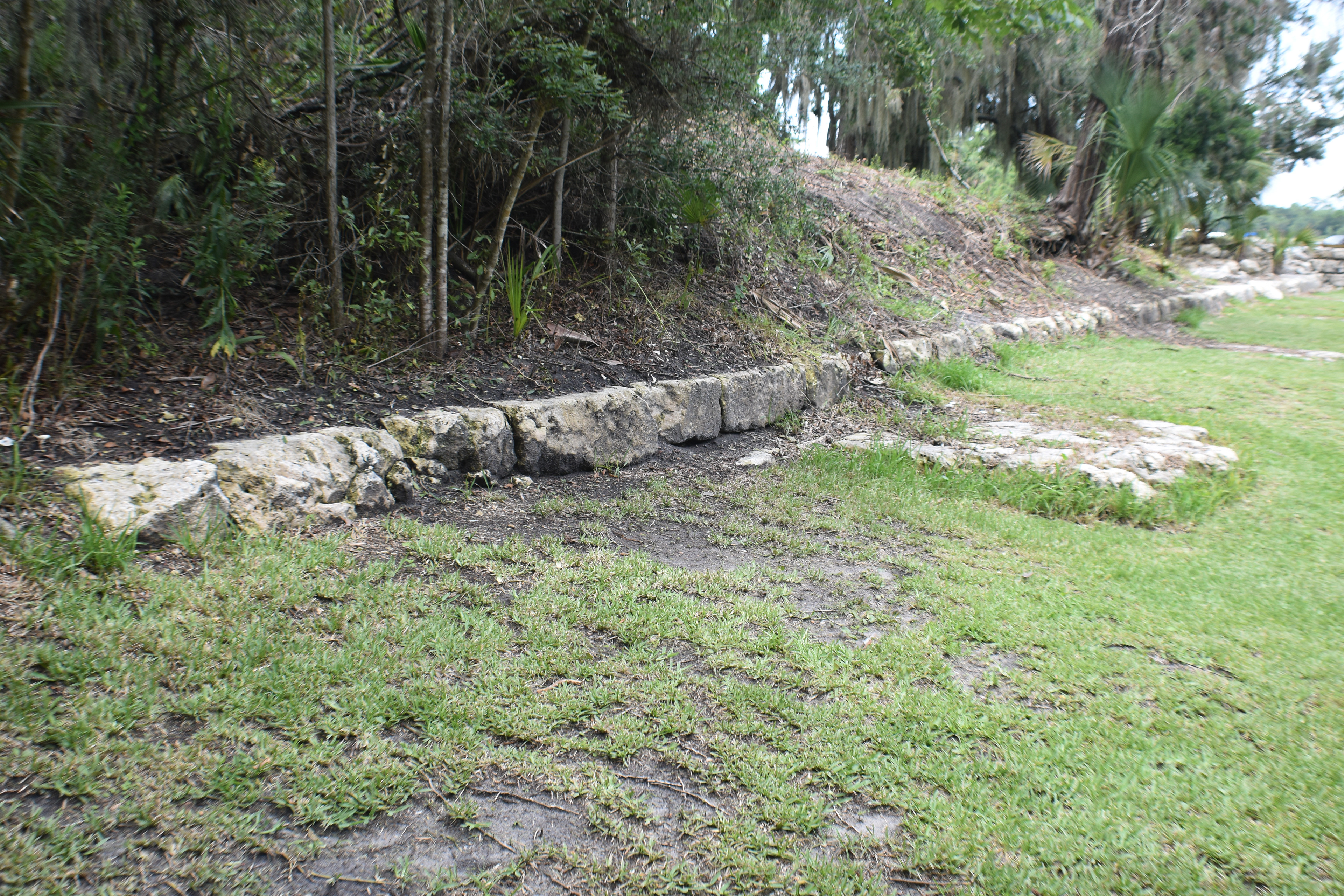
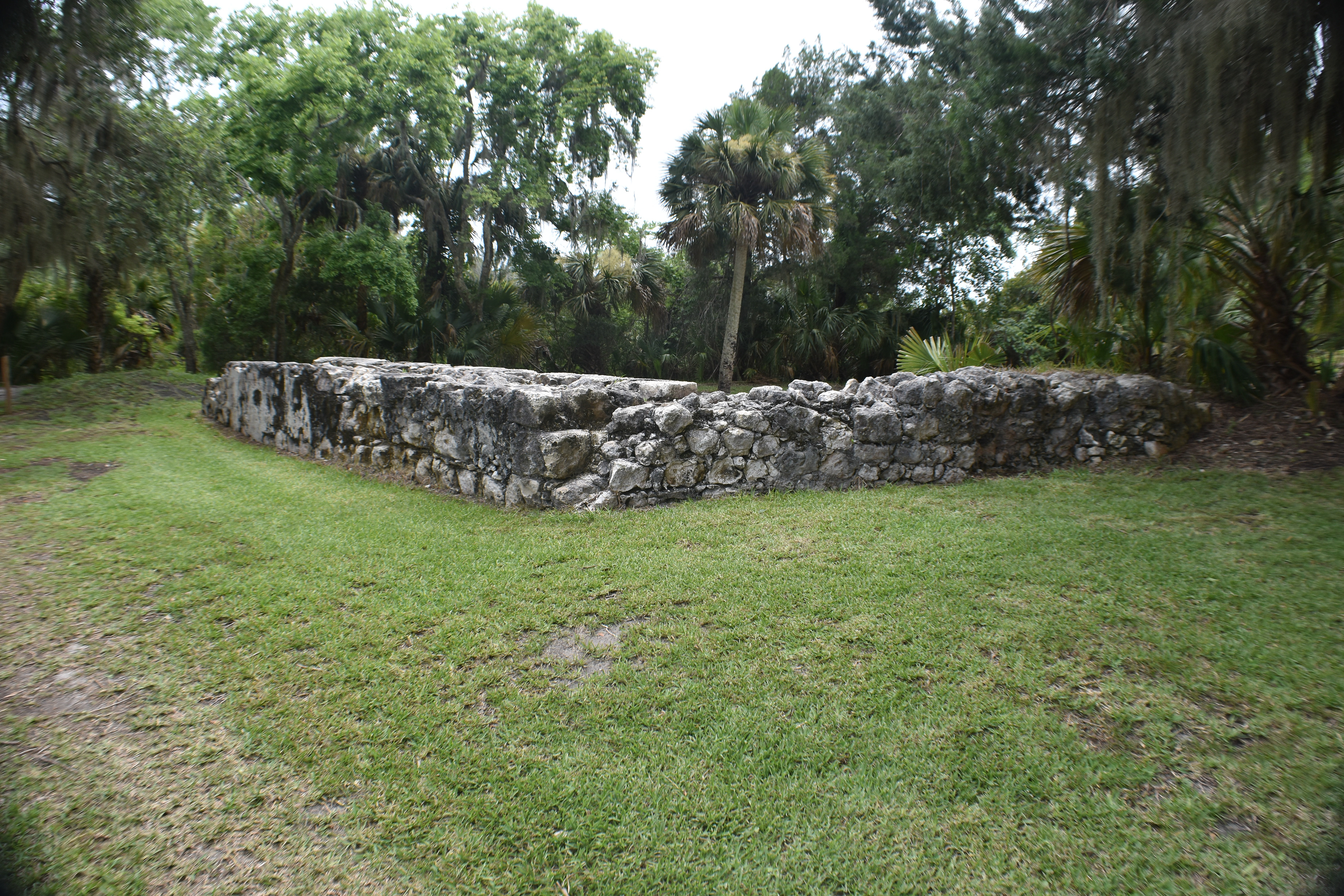
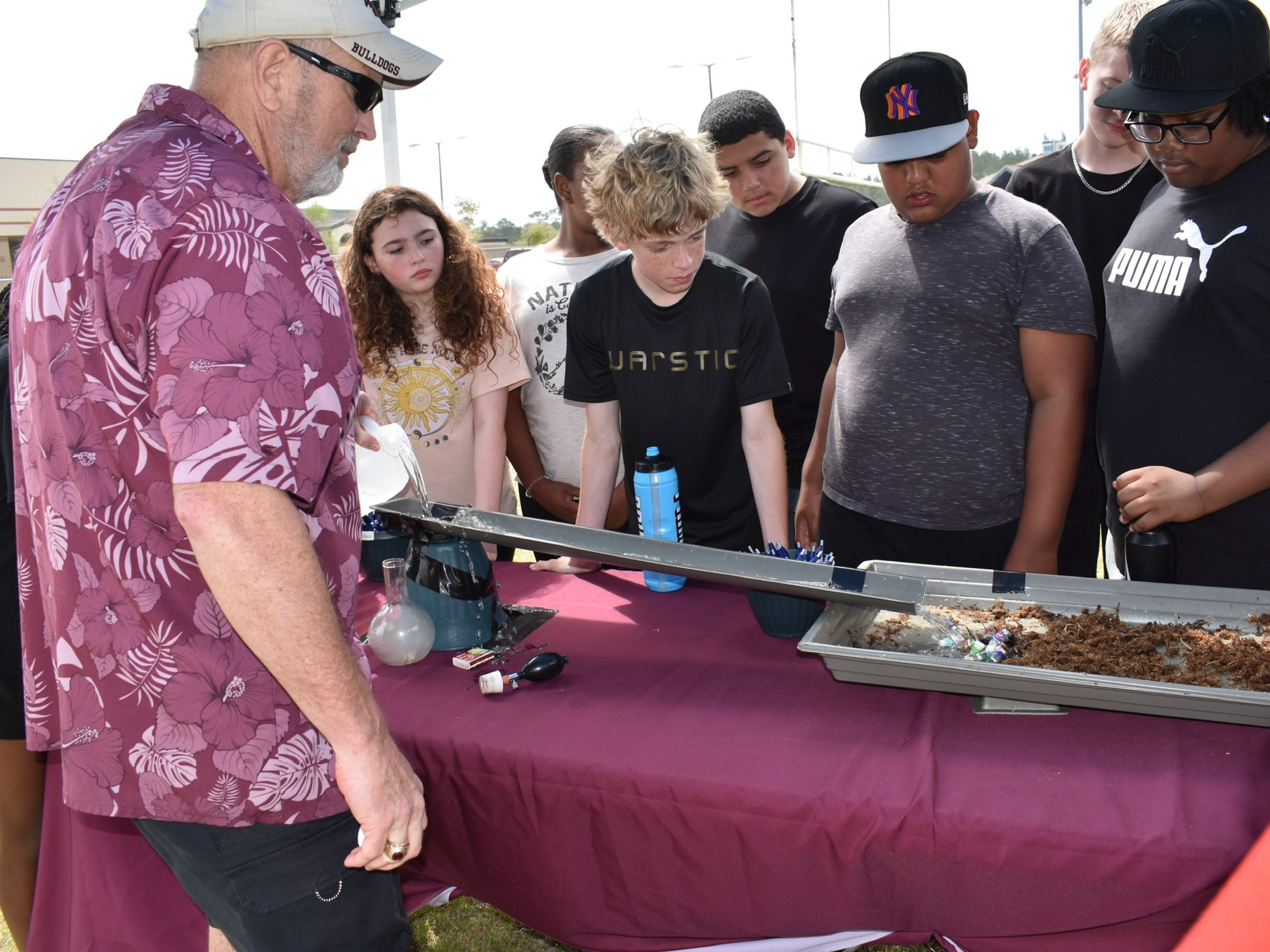
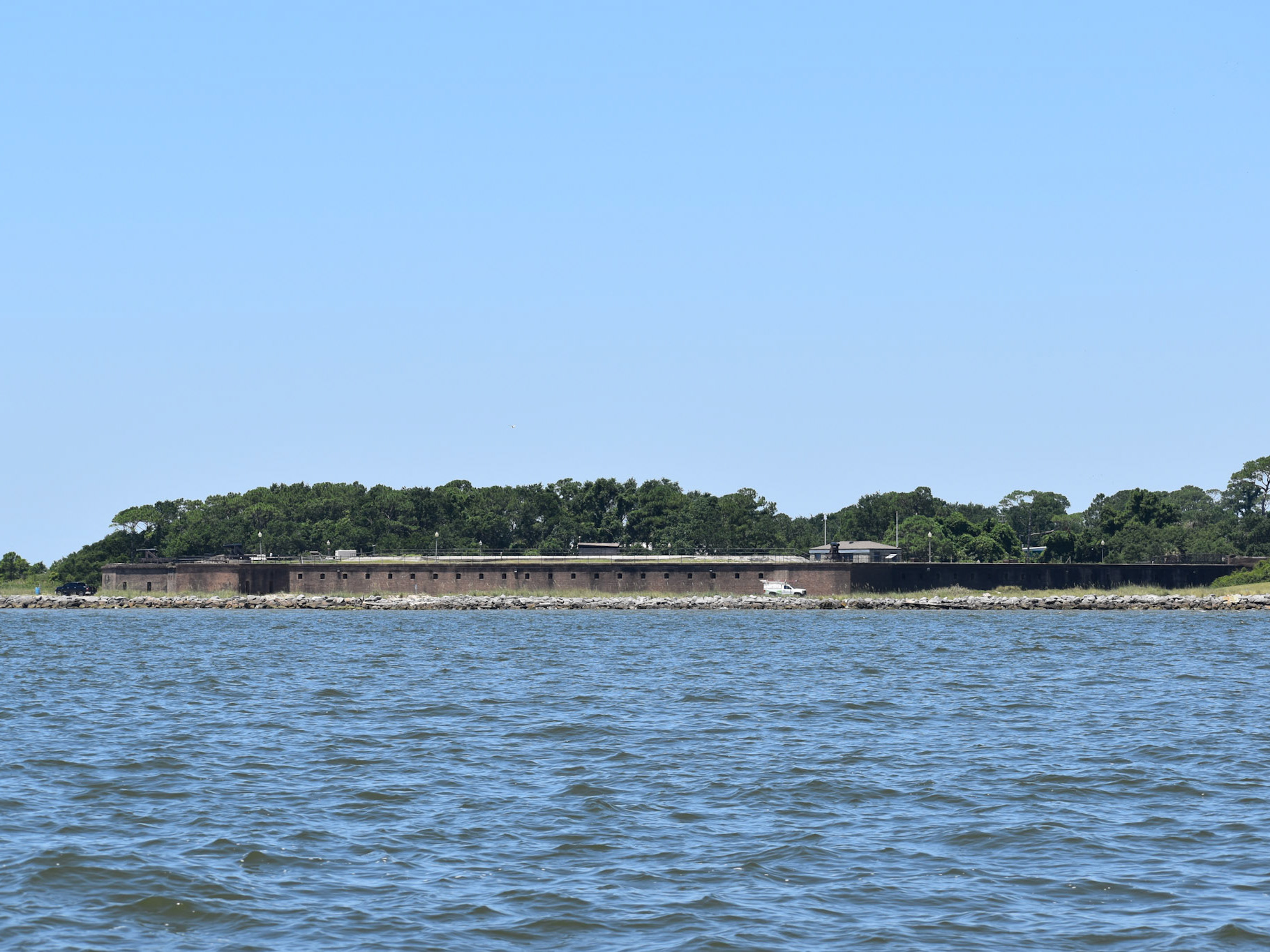
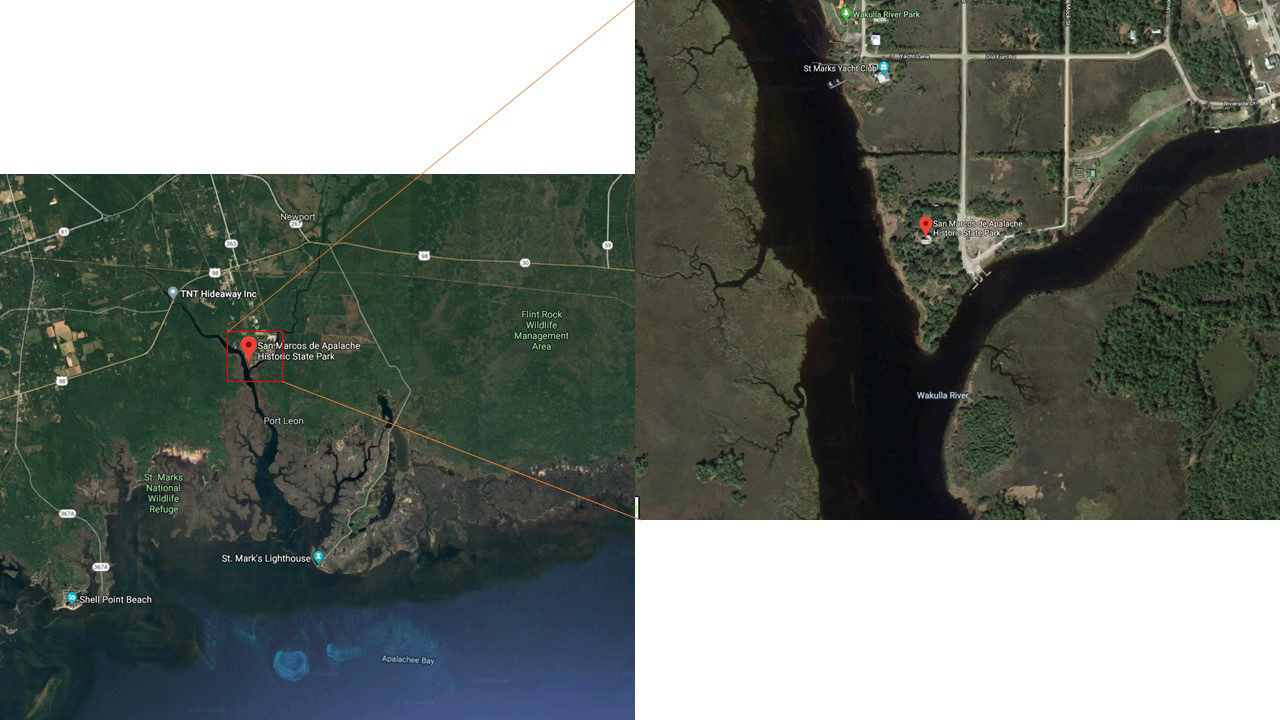
San Marcos de Apalache is a Spanish colonial fort also known as Fort St Marks for the City within which it now resides. The original Spanish construct was composed of wooden buildings and a stockade built in the late 17th century. The original fortification was destroyed by a hurricane which also drowned the entire Spanish Garrison.
This fortification lies near what is considered to be the Native American city of Anhaica which was used as a winter Bivouac for Hernando de Soto in his quest for gold before he moved north through Georgia.
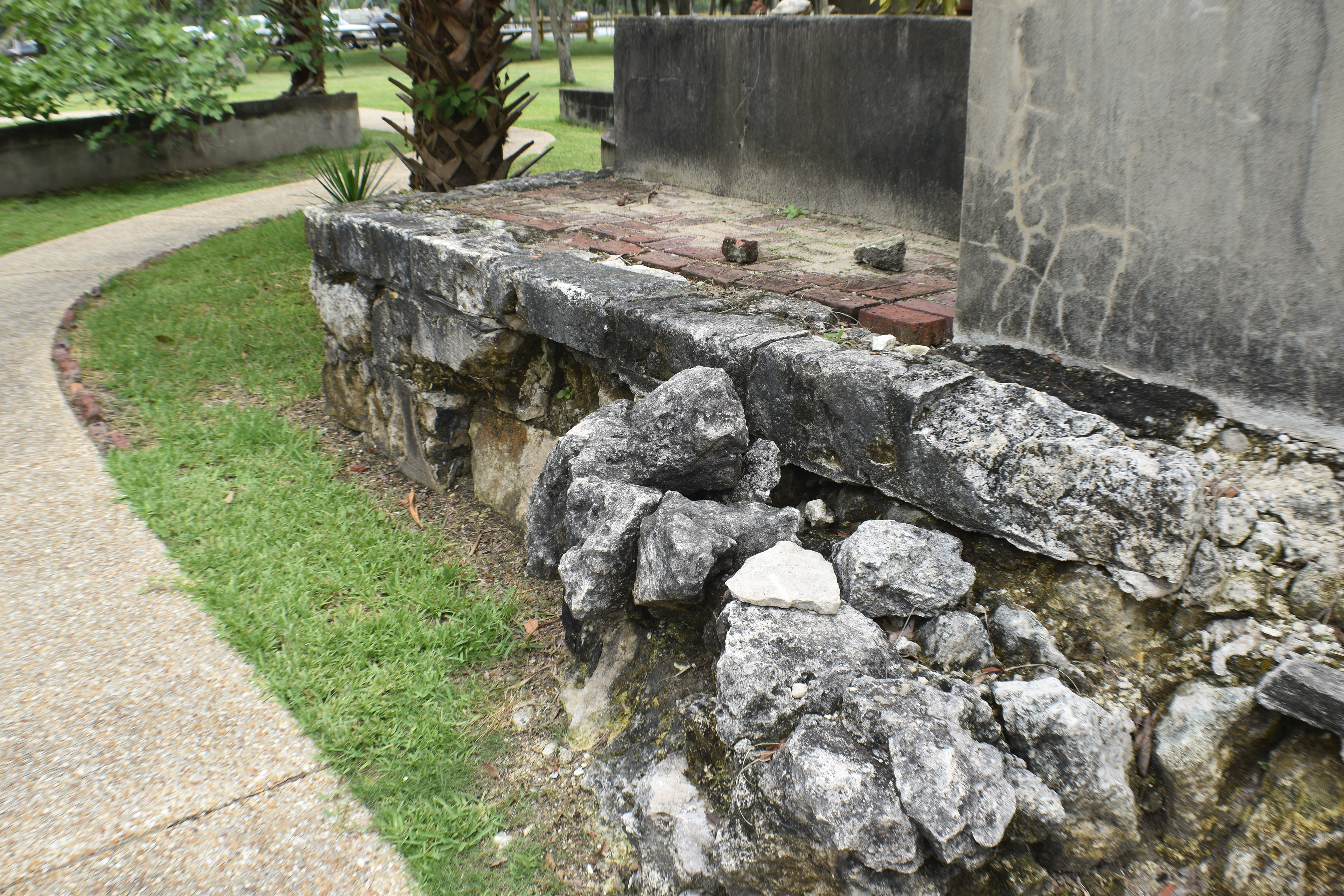
The remains of the stone fort on site were originally constructed by the Spanish in 1753. Following its occupation by Spain, it was shortly occupied by Great Britain before returning to Spanish control. It was later taken by Andrew Jackson for the United States and, occupied by the Confederacy as a hospital, before being returned to U.S. control.
While occupied by the U.S. Military The Fort St. Marks Military Cemetery was established. A total of 19 U.S. Servicemen were buried here.